How Do Search Engines Rank Pages?

How do search engines rank pages?
Search engines rank pages by crawling and indexing content, then using algorithms to evaluate hundreds of ranking factors such as relevance, content quality, backlinks, user experience, page speed, mobile-friendliness, and search intent. Pages that best satisfy user intent and demonstrate authority and trust rank higher in search results.
Search engines play a critical role in how people discover information online. Every day, billions of searches are performed on Google, Bing, and other search engines, yet only a small percentage of web pages ever appear on the first page of results.
So, how do search engines rank pages, and why do some websites consistently outrank others?
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn exactly how search engines work, from crawling and indexing to ranking algorithms, and how you can optimise your website to rank higher in search results.
What Is Search Engine Ranking?
Search engine ranking refers to the position of a web page in the search engine results pages (SERPs) for a specific query. Pages ranking higher (especially in the top three positions) receive significantly more traffic, clicks, and conversions than lower-ranking pages.
Search engines aim to provide users with:
- The most relevant
- The most trustworthy
- The best user experience
Understanding how rankings are determined is the foundation of effective SEO.
How Search Engines Work: The 3 Core Stages
Before ranking any page, search engines follow three essential steps:
- Crawling
- Indexing
- Ranking
Let’s explore each stage in detail.
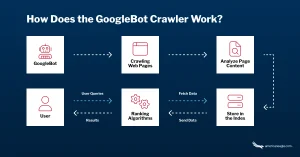
1. Crawling: How Search Engines Discover Content
Crawling is the process by which search engines discover new and updated web pages. Automated programs called crawlers or spiders (such as Googlebot) systematically browse the web by following links.
What Crawlers Look For
- New pages
- Updated content
- Broken links
- Redirects
- Site structure
Factors That Affect Crawling
- Internal linking
- XML sitemaps
- Robots.txt rules
- Page load speed
- Server errors
If a page cannot be crawled, it cannot rank, no matter how good the content is.
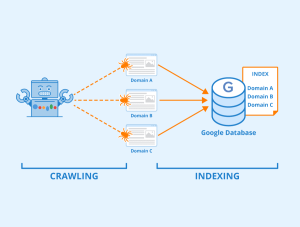
2. Indexing: Storing and Understanding Content
Once a page is crawled, search engines analyse its content and store it in a massive database known as the search index.
During indexing, search engines evaluate:
- Text content
- Images and videos
- Headings and metadata
- Structured data
- Canonical URLs
Why Pages May Not Be Indexed
- Duplicate content
- Thin or low-quality pages
- Noindex tags
- Poor internal linking
- Crawl budget issues
Only indexed pages are eligible to appear in search results.
3. Ranking: How Algorithms Order Search Results
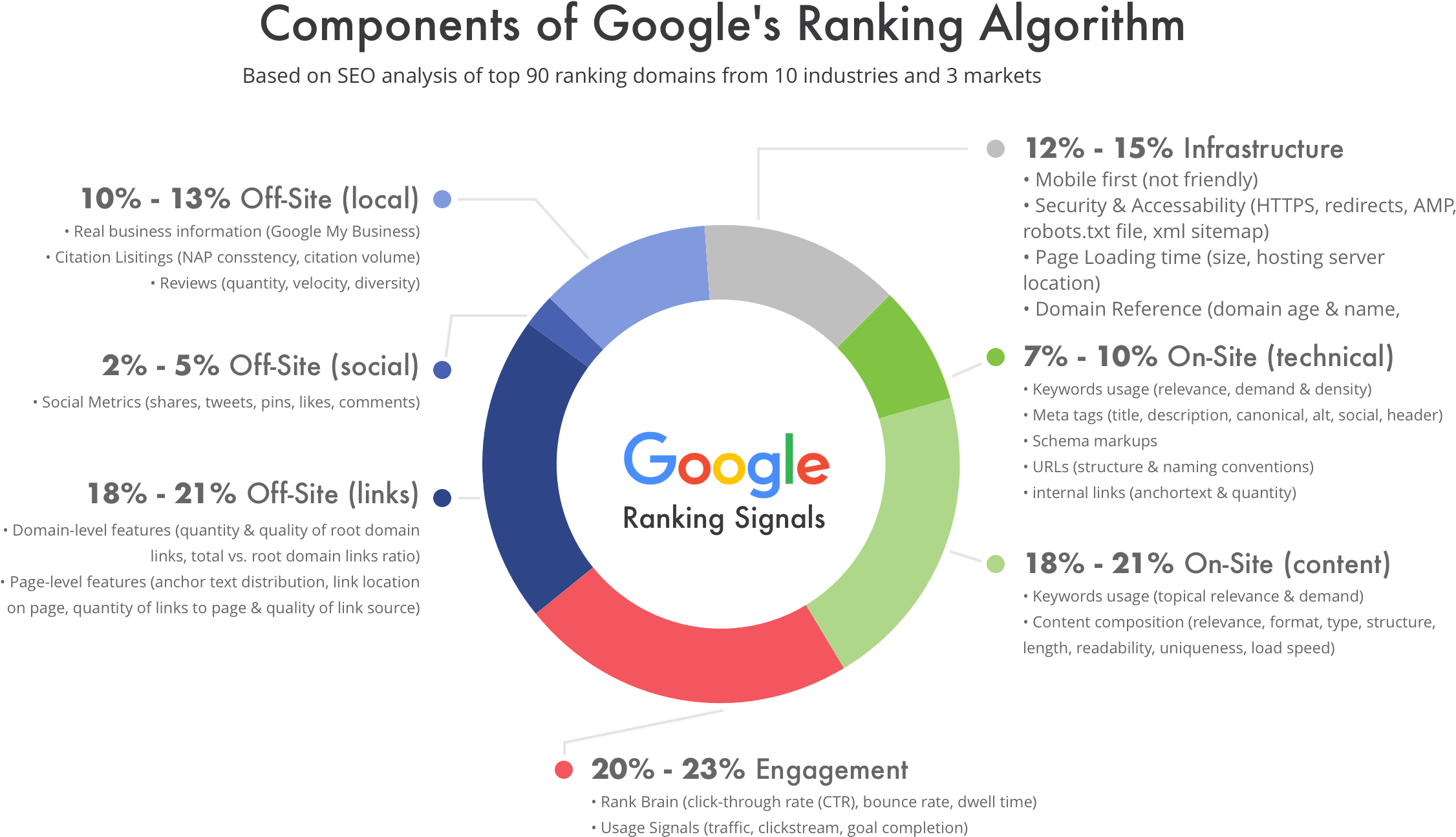
Google alone uses hundreds of ranking factors, and its algorithm is constantly updated to improve accuracy and fight spam.
Key Search Engine Ranking Factors Explained

While no one outside Google knows the exact algorithm, SEO experts agree on several core ranking categories.
1. Search Intent and Relevance
Search engines prioritise pages that best match user intent.
There are four main types of search intent:
- Informational (learn something)
- Navigational (find a specific site)
- Commercial (compare options)
- Transactional (buy or convert)
How to Optimise for Search Intent
- Analyse top-ranking pages
- Match content format (blog, guide, product page)
- Answer user questions clearly
- Use relevant keywords naturally
Relevance is the foundation of ranking.
2. Content Quality and Depth
Content remains one of the strongest ranking factors.
High-quality content is:
- Original and unique
- Comprehensive and in-depth
- Well-structured with headings
- Regularly updated
- Helpful to users
Google’s E-E-A-T framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is central to evaluating content quality.
3. Keywords and On-Page SEO
Keywords help search engines understand what a page is about.
Key On-Page SEO Elements
- Title tags
- Meta descriptions
- H1–H6 headings
- URL structure
- Image alt text
- Internal links
Keyword stuffing no longer works. Modern SEO focuses on semantic relevance and topic coverage rather than exact-match repetition.
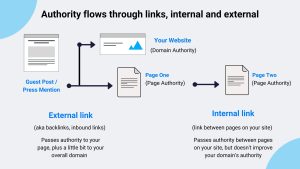
4. Backlinks and Authority
Backlinks are links from other websites pointing to your page. They act as votes of confidence.
What Makes a Backlink Valuable
- Comes from an authoritative site
- Is topically relevant
- Is editorial (not paid or spammy)
- Uses natural anchor text
A few high-quality backlinks often outperform hundreds of low-quality ones.
5. User Experience (UX) Signals
Search engines measure how users interact with your site.
Key UX signals include:
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Bounce rate
- Dwell time
- Page navigation
If users quickly return to search results, it may indicate your page didn’t meet their expectations.
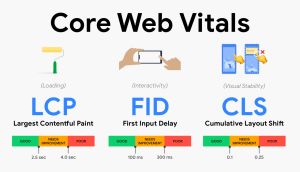
6. Core Web Vitals and Page Speed
Google’s Core Web Vitals evaluate real-world user experience:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) – loading speed
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP) – responsiveness
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) – visual stability
Fast, stable, and responsive pages rank better, especially on mobile.
7. Mobile-Friendliness
With mobile-first indexing, Google primarily evaluates the mobile version of your site.
Mobile optimisation includes:
- Responsive design
- Readable font sizes
- Tap-friendly buttons
- Fast mobile load times
If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, rankings will suffer.
8. Technical SEO Factors
Technical SEO ensures search engines can crawl, index, and rank your site efficiently.
Important technical factors:
- HTTPS security
- Clean URL structure
- XML sitemaps
- Schema markup
- Canonical tags
- Proper redirects
Technical issues can block rankings even if your content is excellent.
How Often Do Search Engine Rankings Change?
Search rankings are dynamic, not static.
They change due to:
- Algorithm updates
- Competitor improvements
- New backlinks
- Content updates
- Shifts in user behaviour
Google makes thousands of algorithm adjustments each year, ranging from minor tweaks to major core updates.
Common Myths About Search Engine Rankings
❌ Myth: SEO is a one-time task
✅ Reality: SEO is ongoing and cumulative
❌ Myth: More keywords = better rankings
✅ Reality: Relevance and quality matter more
❌ Myth: Rankings depend only on backlinks
✅ Reality: UX, content, and intent are equally critical
How to Improve Your Page Rankings (Actionable Tips)
To improve your rankings:
- Create intent-focused, high-quality content
- Optimise on-page SEO elements
- Improve page speed and UX
- Earn authoritative backlinks
- Fix technical SEO issues
- Update content regularly
- Track performance with Search Console
SEO success comes from consistency, not shortcuts.
Conclusion: How Search Engines Rank Pages
Search engines rank pages by analysing relevance, content quality, authority, user experience, and technical performance. While algorithms continue to evolve, the core goal remains the same: deliver the best possible answer to every search query.
By focusing on users first, and optimising for search engines second, you build a site that not only ranks well but also delivers real value.